Water softener PE salt box is mainly used to hold high concentration salt water and reactivate resin. At present, the most common water softener water treatment technology on the market is ion exchange technology. The ion exchange resin in the water softener is usually a sodium sulfonate ion exchange resin. After the raw water to be treated passes through the resin, the calcium and magnesium impurities in the water can be adsorbed in the resin to purify the water.
With the increase of water treatment capacity, more and more impurities are adsorbed, the adsorption capacity of the resin will gradually decrease, and the resin will gradually enter a state of failure. In order to remove the impurities adsorbed by the resin, it is necessary to replace the calcium and magnesium impurities adsorbed by the resin through ion exchange with sodium ions, that is, the sodium ion component in the soft water salt, and restore the adsorption capacity of the ion exchange resin by backwashing. This process is also known as ion exchange resin regeneration.
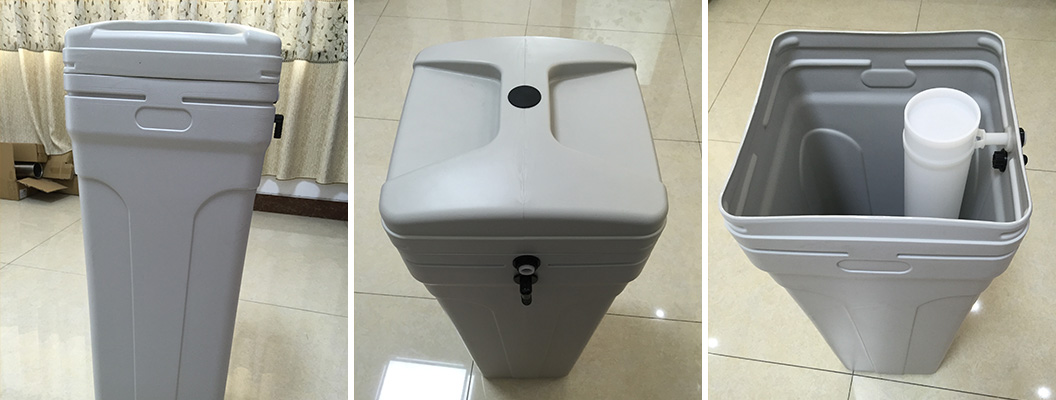

It can be seen that the soft water salt in the PE salt box plays an important role in the water softener. If there is no softening salt in the water softener, the resin will gradually fail, and the corresponding water softener will lose its function of softening and purifying water quality. It must be noted that ordinary edible salt cannot be used in the water softener, and special salt for water softener needs to be used. Due to the strong permeability of iodine to the surface of resin particles, the long-term use of iodine salt will reduce the surface strength, hardness, mechanical strength, volume expansion strength and circular curvature of the resin, and the resin is easy to break, thereby reducing the exchange capacity of the resin.
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português русский
русский français
français 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands ไทย
ไทย Polski
Polski 한국어
한국어 Svenska
Svenska magyar
magyar Malay
Malay বাংলা
বাংলা Dansk
Dansk Suomi
Suomi हिन्दी
हिन्दी Pilipino
Pilipino Türk
Türk Gaeilge
Gaeilge عربى
عربى Indonesia
Indonesia norsk
norsk اردو
اردو čeština
čeština Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Українська
Українська Javanese
Javanese فارسی
فارسی தமிழ்
தமிழ் తెలుగు
తెలుగు नेपाली
नेपाली Burmese
Burmese български
български ລາວ
ລາວ Latine
Latine Қазақ
Қазақ Euskal
Euskal Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan slovenský
slovenský Македонски
Македонски Lietuvos
Lietuvos Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel Română
Română Slovenski
Slovenski मराठी
मराठी Српски
Српски 简体中文
简体中文 Esperanto
Esperanto Afrikaans
Afrikaans Català
Català עִברִית
עִברִית Cymraeg
Cymraeg Galego
Galego 繁体中文
繁体中文 Latvietis
Latvietis icelandic
icelandic יידיש
יידיש Беларус
Беларус Hrvatski
Hrvatski Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen Shqiptar
Shqiptar Malti
Malti lugha ya Kiswahili
lugha ya Kiswahili አማርኛ
አማርኛ Bosanski
Bosanski Frysk
Frysk ជនជាតិខ្មែរ
ជនជាតិខ្មែរ ქართული
ქართული ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી Hausa
Hausa Кыргыз тили
Кыргыз тили ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ Corsa
Corsa Kurdî
Kurdî മലയാളം
മലയാളം Maori
Maori Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл Hmong
Hmong IsiXhosa
IsiXhosa Zulu
Zulu Punjabi
Punjabi پښتو
پښتو Chichewa
Chichewa Samoa
Samoa Sesotho
Sesotho සිංහල
සිංහල Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig Cebuano
Cebuano Somali
Somali Точик
Точик O'zbek
O'zbek Hawaiian
Hawaiian سنڌي
سنڌي Shinra
Shinra հայերեն
հայերեն Igbo
Igbo Sundanese
Sundanese Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch Malagasy
Malagasy Yoruba
Yoruba