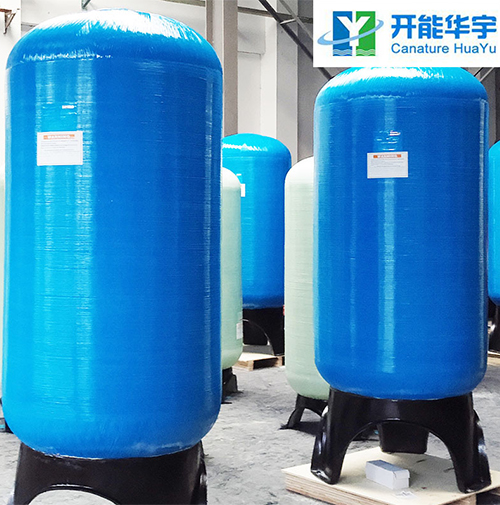
The softening resin tank is a tank used to remove hardness ions such as calcium and magnesium in water and soften the water. The most common is the glass fiber reinforced plastic softening resin tank, which is often used in water treatment occasions such as laundry rooms, hotels, chemicals, textiles and so on.
The control methods of the FRP softening resin tank are as follows: A. It consists of an ion exchange tank, a control valve and a salt tank. The regeneration control mode is divided into time type and flow type. During regeneration, water production needs to be stopped for 2 hours.
It is suitable for intermittent water supply occasions. If continuous water supply is required, a water tank can be configured to store water for 2 hours. B. Two ion exchange tanks are controlled by one control valve to supply water alternately and regenerate alternately to realize uninterrupted water supply. It is suitable for the occasion of continuous water supply. The regeneration method is flow type.
It consists of two control valves, two ion exchange tanks and a salt tank. The two sets of tanks are alternately supplied with water, alternately regenerated, and continuously supplied with water. The regeneration control mode is flow type.
It consists of two control valves, two ion exchange tanks, and two salt tanks. The two sets of tanks supply water at the same time, alternately regenerate, and continuously supply water. The regeneration control mode is flow type.
How to choose the appropriate control method for the FRP softening resin tank should be determined according to the actual processing capacity. If the processing capacity of the FRP softening resin tank is small, a single ion exchange tank and single valve control can be selected. If the processing capacity is large, multiple Ion exchange tank treatment.

 English
English Español
Español Português
Português русский
русский français
français 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands ไทย
ไทย Polski
Polski 한국어
한국어 Svenska
Svenska magyar
magyar Malay
Malay বাংলা
বাংলা Dansk
Dansk Suomi
Suomi हिन्दी
हिन्दी Pilipino
Pilipino Türk
Türk Gaeilge
Gaeilge عربى
عربى Indonesia
Indonesia norsk
norsk اردو
اردو čeština
čeština Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Українська
Українська Javanese
Javanese فارسی
فارسی தமிழ்
தமிழ் తెలుగు
తెలుగు नेपाली
नेपाली Burmese
Burmese български
български ລາວ
ລາວ Latine
Latine Қазақ
Қазақ Euskal
Euskal Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan slovenský
slovenský Македонски
Македонски Lietuvos
Lietuvos Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel Română
Română Slovenski
Slovenski मराठी
मराठी Српски
Српски 简体中文
简体中文 Esperanto
Esperanto Afrikaans
Afrikaans Català
Català עִברִית
עִברִית Cymraeg
Cymraeg Galego
Galego 繁体中文
繁体中文 Latvietis
Latvietis icelandic
icelandic יידיש
יידיש Беларус
Беларус Hrvatski
Hrvatski Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen Shqiptar
Shqiptar Malti
Malti lugha ya Kiswahili
lugha ya Kiswahili አማርኛ
አማርኛ Bosanski
Bosanski Frysk
Frysk ជនជាតិខ្មែរ
ជនជាតិខ្មែរ ქართული
ქართული ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી Hausa
Hausa Кыргыз тили
Кыргыз тили ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ Corsa
Corsa Kurdî
Kurdî മലയാളം
മലയാളം Maori
Maori Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл Hmong
Hmong IsiXhosa
IsiXhosa Zulu
Zulu Punjabi
Punjabi پښتو
پښتو Chichewa
Chichewa Samoa
Samoa Sesotho
Sesotho සිංහල
සිංහල Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig Cebuano
Cebuano Somali
Somali Точик
Точик O'zbek
O'zbek Hawaiian
Hawaiian سنڌي
سنڌي Shinra
Shinra հայերեն
հայերեն Igbo
Igbo Sundanese
Sundanese Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch Malagasy
Malagasy Yoruba
Yoruba